Bitcoin cryptocurrency, a revolutionary digital currency, has captivated global attention. Its decentralized nature and cryptographic security have sparked both excitement and skepticism. This exploration delves into the multifaceted aspects of Bitcoin, from its technological underpinnings to its economic impact and future prospects.
Bitcoin’s origins lie in the desire for a peer-to-peer electronic cash system, free from the constraints of traditional banking. This digital gold standard, powered by blockchain technology, promises secure and transparent transactions, while its volatility presents unique investment challenges.
Introduction to Bitcoin: Bitcoin Cryptocurrency

Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency, operating independently of central banks and financial institutions. It relies on a distributed ledger technology called blockchain to record and verify transactions. This eliminates intermediaries and promotes transparency and security.Bitcoin’s design is based on cryptographic principles, enabling secure and verifiable transactions without a central authority. This decentralized nature makes it resistant to censorship and manipulation.
It has revolutionized the way individuals and businesses interact in the digital economy.
Bitcoin’s Fundamental Principles, Bitcoin cryptocurrency
Bitcoin’s core principles underpin its functionality and security. These principles ensure the integrity and transparency of the network. Decentralization is key, with no single entity controlling the system.
- Decentralization: Bitcoin operates without a central authority. Transactions are verified and recorded by a network of computers, preventing any single point of failure or control.
- Cryptography: Cryptographic hashing and digital signatures are fundamental to Bitcoin’s security. They ensure the integrity of transactions and prevent fraudulent activities.
- Blockchain: Bitcoin uses a distributed ledger called blockchain to record transactions. This ensures transparency and immutability, making it difficult to alter or manipulate past records.
Role of Cryptography in Bitcoin Security
Cryptography plays a crucial role in safeguarding Bitcoin transactions. It ensures the integrity and confidentiality of data exchanged within the network.Bitcoin utilizes cryptographic hashing algorithms to generate unique identifiers for transactions. These identifiers are then linked together in a chain, forming the blockchain. Digital signatures are employed to verify the authenticity of transactions. These techniques make tampering with Bitcoin transactions extremely difficult.
Historical Overview of Bitcoin’s Development
Bitcoin’s journey began with a whitepaper published in 2008 by Satoshi Nakamoto, a pseudonymous developer or group of developers. This document Artikeld the core concepts of the cryptocurrency.
- 2008: Satoshi Nakamoto publishes the Bitcoin whitepaper, laying the foundation for the cryptocurrency.
- 2009: The first Bitcoin transaction occurs, marking the genesis of the Bitcoin network.
- Subsequent Years: Bitcoin’s adoption and use have grown steadily, facing challenges and controversies along the way, such as volatility and regulatory concerns. The continued development and adoption of blockchain technology have further advanced Bitcoin’s impact on the financial landscape.
Bitcoin’s Technology
Bitcoin’s revolutionary nature stems from its innovative underlying technology, the blockchain. This distributed ledger system ensures transparency and security in transactions, while also enabling decentralized control. This technology, combined with cryptographic principles, forms the bedrock of Bitcoin’s functionality and its unique characteristics.
Blockchain Technology
The blockchain is a continuously growing list of records, called blocks, that are linked together using cryptography. Each block contains a batch of Bitcoin transactions, along with a timestamp and a cryptographic hash of the previous block. This chain-like structure makes it extremely difficult to alter past records, as any change would require altering all subsequent blocks, which would be immediately detectable.
Bitcoin Transaction Process
Bitcoin transactions are initiated when a user wants to send Bitcoin to another user. This transaction is broadcast to the Bitcoin network, where nodes verify its validity. The verification process involves checking the sender’s balance and ensuring the transaction hasn’t already been spent. Once validated, the transaction is added to a block, and the new balance for both the sender and recipient is updated on the blockchain.
Transaction Validation Mechanisms
Bitcoin transactions are validated by a network of nodes, which operate independently. These nodes verify the authenticity of the transaction signatures and the sender’s available balance. Validation involves checking for double-spending attempts, where a user tries to spend the same Bitcoin multiple times. This process employs cryptographic techniques to guarantee the integrity and security of transactions. Crucially, the consensus mechanism ensures that all nodes agree on the validity of a transaction.
Mining and Consensus Mechanisms
Bitcoin mining is the process of adding new blocks to the blockchain. Miners compete to solve complex cryptographic puzzles, and the first miner to solve the puzzle gets to add the block to the chain, receiving newly created Bitcoin as a reward. This process is crucial for maintaining the integrity and security of the Bitcoin network. Proof-of-work (PoW) is the consensus mechanism employed by Bitcoin, requiring miners to perform substantial computational work to validate transactions and add blocks to the blockchain.
This ensures that the network remains secure and resistant to attacks. For example, a significant increase in computational power required for mining would effectively increase the difficulty for malicious actors to manipulate the network.
Bitcoin’s Economic Impact
Bitcoin’s emergence as a digital currency has sparked significant debate and discussion regarding its economic implications. While promising as a potential alternative to traditional currencies, its inherent volatility and decentralized nature pose unique challenges. Understanding these facets is crucial to assessing Bitcoin’s true impact on the global economy.Bitcoin’s potential as a currency rests on its decentralized and borderless nature.
It operates independently of central banks, allowing for transactions globally without intermediaries, theoretically reducing transaction costs and enabling access to financial services for unbanked populations.
Bitcoin, a popular cryptocurrency, needs a secure place to store your holdings. A good cryptocurrency wallet is essential for managing and safeguarding your bitcoin. Ultimately, a robust digital wallet is crucial for safely handling your bitcoin investments.
Potential Benefits of Bitcoin
Bitcoin offers the potential for reduced transaction costs and fees compared to traditional banking systems. This is due to its decentralized nature, eliminating the need for intermediaries. Furthermore, it provides financial inclusion to individuals who lack access to traditional banking services. This is particularly relevant in developing nations where access to banking infrastructure is limited.
Potential Risks Associated with Bitcoin’s Volatility
Bitcoin’s price fluctuations can be extreme and unpredictable. This volatility poses a significant risk to investors, as the value of Bitcoin holdings can fluctuate dramatically in short periods. Examples of significant price swings exist throughout Bitcoin’s history, demonstrating its price instability.
Economic Implications of Bitcoin’s Adoption or Rejection
The adoption of Bitcoin as a mainstream currency would have profound implications for traditional financial systems. This includes challenges to the existing banking infrastructure, as well as the potential for new financial opportunities. Conversely, rejection could lead to the marginalization of Bitcoin, limiting its economic role.
Impact on Traditional Financial Systems
Bitcoin’s decentralized structure challenges the traditional centralized banking model. This creates both opportunities and threats to existing financial institutions. For example, the emergence of crypto-friendly banks and payment systems illustrates a response to Bitcoin’s increasing presence. This evolution highlights a possible shift towards more decentralized financial systems.
Bitcoin’s Market Analysis
Bitcoin’s market is a dynamic and complex ecosystem, characterized by significant price volatility and a wide range of participant motivations. Understanding the forces driving these fluctuations is crucial for anyone looking to navigate this space. Market analysis considers factors like investor sentiment, regulatory changes, technological advancements, and global economic conditions to predict future trends.
Overview of the Bitcoin Market
The Bitcoin market encompasses a broad spectrum of activities, including trading, investment, and speculation. It is a decentralized market, meaning it operates outside the control of any single entity. This characteristic contributes to both its allure and its inherent risks. Market participants range from individual investors to large institutional players, creating a complex interplay of forces that shape the market’s trajectory.
The market’s structure influences how information spreads, impacting price and sentiment. The transparency of the blockchain, while promoting trust, can also make the market susceptible to rapid shifts in price based on collective perception.
Factors Influencing Bitcoin’s Price Fluctuations
Numerous factors influence Bitcoin’s price, creating a volatile environment. These factors often interact in complex ways, making precise prediction challenging. News and events, both within and outside the cryptocurrency space, can significantly impact the price. For example, regulatory announcements, especially those regarding stricter regulations, tend to create periods of uncertainty and volatility.
Role of Speculation and Investment
Speculation plays a substantial role in Bitcoin’s price movements. Speculators often enter the market based on perceived future price increases. This can create upward or downward pressure on the price, depending on the collective sentiment of market participants. Alongside speculation, investment plays a vital role, with some investors purchasing Bitcoin as a long-term asset, hoping to profit from its potential growth.
The interplay between speculative activity and long-term investment strategies significantly impacts the market’s overall direction.
Comparison to Other Cryptocurrencies
Bitcoin, while the first and most well-known cryptocurrency, is not the only option in the market. Many other cryptocurrencies exist, each with its own unique characteristics and potential applications. Comparison involves examining factors like market capitalization, technology, and use cases. A comparison table provides a structured overview of different cryptocurrencies, enabling a deeper understanding of the competitive landscape and their relative strengths.
Comparison Table: Bitcoin vs. Selected Cryptocurrencies
| Characteristic | Bitcoin | Ethereum | Tether |
|---|---|---|---|
| Market Capitalization | Large | Large | Medium |
| Technology | Decentralized, proof-of-work | Decentralized, proof-of-stake | Stablecoin, pegged to fiat |
| Use Cases | Digital currency, store of value | Smart contracts, decentralized applications | Currency exchange, stable value |
The table above provides a simplified comparison, highlighting key distinctions. Further research into each cryptocurrency’s specific characteristics is necessary for a complete understanding.
Bitcoin and Regulation

Bitcoin’s decentralized nature presents unique challenges for regulatory bodies worldwide. Governments grapple with balancing the potential benefits of innovation with the need to protect investors and maintain financial stability. The absence of a single global regulatory framework creates a complex and fragmented landscape for Bitcoin businesses and users.
Current Regulatory Landscape
The global regulatory landscape for Bitcoin is diverse and often inconsistent. Some jurisdictions have embraced Bitcoin with regulatory sandboxes and licensing frameworks, while others have taken a more cautious approach, sometimes even outright banning or restricting its use. The lack of a unified approach creates uncertainty for businesses operating across borders. For example, some countries view Bitcoin as a currency, while others treat it as a commodity or security, leading to differing tax implications and legal interpretations.
Challenges in Regulating Bitcoin
Several key challenges hinder the effective regulation of Bitcoin. The decentralized nature of the technology makes it difficult to enforce regulations on a global scale. Moreover, the rapid evolution of Bitcoin’s ecosystem and related technologies presents a constant challenge to regulators in keeping pace. Another challenge is the technical complexity of the technology itself, making it difficult for regulators to fully understand and assess its risks and benefits.
Finally, the jurisdictional issues surrounding Bitcoin transactions, which often span multiple countries, complicate the enforcement of any regulatory framework.
Potential Impact of Regulations on the Bitcoin Market
Regulations can have a profound impact on the Bitcoin market. Positive regulations, such as clear guidelines and licensing frameworks, can foster trust and attract institutional investment, potentially driving market growth. Conversely, overly restrictive regulations or those that lack clarity can stifle innovation and discourage participation, potentially hindering the market’s development. Examples from other industries, like the internet or financial services, illustrate how poorly designed regulations can stifle growth and innovation.
The recent history of regulatory changes in other financial markets shows the potential for both positive and negative consequences.
Possible Regulatory Framework for Bitcoin
A possible regulatory framework for Bitcoin should prioritize clarity, consistency, and adaptability. It should recognize the unique characteristics of Bitcoin while addressing the concerns of investors and financial stability.
- Defining Bitcoin’s Legal Status: Clear definitions are crucial for consistent enforcement. Classifying Bitcoin as a commodity, currency, or security will impact how it is taxed and regulated, which will affect its acceptance and usage. Similar classifications of other digital assets could serve as precedents.
- Establishing Licensing and Compliance Requirements: Regulations should Artikel specific licensing requirements for Bitcoin businesses, such as exchanges and custodians. This could involve mandatory KYC/AML procedures, similar to those applied to traditional financial institutions. This approach would also help prevent illicit activities.
- Consumer Protection Measures: Robust consumer protection measures should be in place to safeguard investors. This might include disclosure requirements for Bitcoin offerings and platforms, and limitations on high-risk investment products. Existing consumer protection laws could be adapted to address specific risks associated with cryptocurrencies.
- International Cooperation: A global approach to regulation is needed. International cooperation and harmonization of regulations would mitigate the complexities associated with cross-border transactions and reduce regulatory arbitrage.
Bitcoin’s Future Prospects
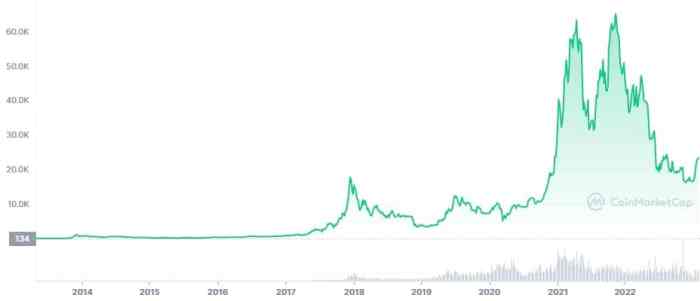
Bitcoin’s trajectory into the future remains a subject of considerable debate and speculation. While its past performance has been notable, predicting its long-term evolution requires careful consideration of various factors, including technological advancements, regulatory landscapes, and market dynamics. The future potential of Bitcoin hinges on its ability to adapt to evolving circumstances and maintain its position as a viable asset.The future of Bitcoin is intertwined with the progression of blockchain technology and its wider adoption across diverse sectors.
Technological advancements will likely shape the very nature of Bitcoin, influencing its functionality and usability. Potential impacts of emerging technologies on Bitcoin’s infrastructure and capabilities will be pivotal in shaping its future.
Potential Advancements in Bitcoin Technology
Bitcoin’s core technology, while revolutionary for its time, has room for improvement. Potential advancements could include increased transaction speeds, enhanced scalability, and improved energy efficiency. These enhancements could make Bitcoin more attractive to a broader range of users and applications. For example, advancements in cryptography could lead to more secure and efficient transaction processing, potentially mitigating some of the existing security concerns.
Likewise, improvements in consensus mechanisms could enhance the network’s resilience and efficiency.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on Bitcoin
Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and quantum computing could significantly impact Bitcoin. AI could be used to analyze market trends and predict price movements, potentially affecting investment strategies. ML algorithms could optimize Bitcoin mining strategies, potentially influencing energy consumption. However, quantum computing poses a potential threat to the security of Bitcoin’s cryptographic system, if not adequately addressed.
Careful consideration of these potential impacts is crucial to understanding the future of Bitcoin.
Potential Scenarios for Bitcoin’s Long-Term Evolution
Several scenarios regarding Bitcoin’s long-term evolution are possible. One scenario envisions Bitcoin as a prominent digital asset, integrated into mainstream financial systems. This scenario assumes continued innovation in the technology and a positive regulatory environment. Another scenario projects Bitcoin as a niche investment, utilized primarily by specialized traders or for specific applications. This scenario may result from regulatory hurdles or technological limitations.
Finally, a scenario of widespread adoption for everyday transactions, similar to traditional currencies, remains possible, but faces significant obstacles.
Bitcoin and Sustainability
Bitcoin’s decentralized nature and global reach have spurred significant discussion regarding its environmental impact, particularly its energy consumption during mining. The increasing adoption of the cryptocurrency has led to a heightened awareness of its potential contribution to climate change, prompting the need for environmentally conscious practices.The energy-intensive nature of Bitcoin mining is a prominent concern. The process of verifying and adding new transactions to the blockchain requires substantial computational power, often relying on specialized hardware.
This process, while securing the network, can translate into significant energy consumption. Understanding the scale of this energy use and comparing it to other financial systems is crucial for assessing the true environmental footprint.
Environmental Impact of Bitcoin Mining
Bitcoin mining’s energy consumption is a significant concern. The process requires substantial computational power to solve complex mathematical problems, securing the network and validating transactions. This process often relies on specialized hardware, which in turn demands a substantial amount of energy. The environmental impact is directly linked to the energy sources used in these operations.
Comparison with Other Financial Systems
The energy consumption of Bitcoin mining stands in contrast to traditional financial systems. While precise comparisons are challenging due to diverse operational methodologies, Bitcoin mining’s energy footprint is substantially higher than traditional banking and payment systems. This difference is primarily attributable to the decentralized, proof-of-work nature of the Bitcoin network, which requires substantial computational power for verification and security.
For example, estimates suggest that Bitcoin’s energy consumption is comparable to that of a small country.
Potential Solutions to Mitigate Environmental Impact
Several approaches aim to mitigate the environmental impact of Bitcoin mining. One potential solution involves transitioning to more sustainable energy sources, such as renewable energy. This approach involves aligning mining operations with renewable energy facilities to reduce the reliance on fossil fuels. A shift towards renewable energy sources could significantly reduce the carbon footprint of Bitcoin mining.
Strategies for Sustainable Bitcoin Mining Practices
Sustainable Bitcoin mining practices encompass a range of strategies. Utilizing renewable energy sources, such as hydroelectric or solar power, can drastically reduce the environmental impact of mining operations. Moreover, enhancing the efficiency of mining hardware and algorithms can also lead to reduced energy consumption. Developing more energy-efficient mining techniques, like transitioning to proof-of-stake consensus mechanisms, are potential solutions to lessen the environmental burden.
Finally, encouraging the use of recycled materials in mining hardware is another environmentally friendly strategy.
Bitcoin and Accessibility
Bitcoin’s decentralized nature aims for global accessibility, but practical factors influence its usability for different groups. This section explores various methods for acquiring Bitcoin, examines accessibility across demographics, provides a practical step-by-step guide, and compares different Bitcoin wallet options.Bitcoin’s potential as a financial tool for underserved populations is significant, but obstacles remain in terms of digital literacy, access to technology, and financial infrastructure.
The accessibility of Bitcoin depends heavily on individual circumstances and the availability of supporting services.
Methods for Acquiring Bitcoin
A range of methods allows individuals to acquire Bitcoin. These include purchasing directly from exchanges, using peer-to-peer platforms, or receiving Bitcoin as payment. Direct purchases offer convenience but typically involve fees and potential exchange rate fluctuations. Peer-to-peer transactions often offer lower fees but necessitate trust and careful verification. Receiving Bitcoin as payment is a growing trend in certain sectors.
- Exchanges: Major cryptocurrency exchanges provide a platform to buy and sell Bitcoin using fiat currencies like USD or EUR. Users create accounts, deposit funds, and initiate trades. Fees and transaction times vary between platforms. Examples include Coinbase, Kraken, and Binance.
- Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Platforms: These platforms connect buyers and sellers directly, enabling transactions without intermediaries. Fees are often lower, but users must vet potential counterparties and handle transactions cautiously. Examples include LocalBitcoins and Paxful.
- Receiving as Payment: Businesses or individuals can accept Bitcoin as payment for goods or services. This is becoming more common, particularly in specific industries.
Accessibility Across Demographics
Bitcoin’s accessibility varies across demographics. Factors such as digital literacy, access to technology, and financial infrastructure significantly influence adoption rates. Younger generations, often more tech-savvy, tend to have higher rates of adoption. Lower-income populations may face barriers due to lack of access to reliable internet or financial services. Efforts to improve digital literacy and financial inclusion are crucial for broader adoption.
- Age Groups: Younger generations, familiar with digital technologies, often demonstrate higher Bitcoin adoption rates compared to older generations. Efforts to bridge the digital divide are essential for broader adoption.
- Geographic Location: Access to financial infrastructure and digital services varies significantly globally. Developing economies may face challenges in adopting Bitcoin due to limitations in access to banking services and reliable internet connectivity.
- Economic Background: Individuals with limited financial resources may encounter barriers to acquiring Bitcoin due to transaction costs or a lack of readily available fiat currency.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using Bitcoin
A basic guide to using Bitcoin involves several steps. First, users need a Bitcoin wallet. Then, they need to fund the wallet with fiat currency through a supported exchange or P2P platform. Finally, they can initiate transactions using their Bitcoin balance.
- Create a Bitcoin Wallet: Download a software or mobile Bitcoin wallet application. Many options exist, ranging from simple wallets to more complex ones with advanced features.
- Fund Your Wallet: Use a supported exchange or P2P platform to buy Bitcoin and transfer it to your chosen wallet. This process often involves verification and compliance checks.
- Initiate Transactions: Use the wallet application to send Bitcoin to another wallet or address. This involves specifying the recipient’s address and the desired amount.
Comparison of Bitcoin Wallets
Various Bitcoin wallets cater to different needs and technical expertise. Factors to consider when choosing a wallet include security, ease of use, features, and fees. A comparison table highlights some of the most popular options.
| Wallet | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Hardware Wallet (e.g., Ledger Nano S) | Enhanced security, offline storage | Higher cost, potential setup complexity |
| Software Wallet (e.g., Electrum) | Open-source, free, customizable | Requires more technical understanding |
| Mobile Wallet (e.g., Blockchain.com) | Convenience, accessible from smartphones | Potentially less secure if not adequately protected |
Bitcoin Use Cases
Bitcoin, initially conceived as a digital currency, has evolved into a versatile technology with diverse applications beyond simple transactions. Its decentralized nature and inherent security features make it a compelling option for various industries and economic contexts. This exploration delves into practical applications, emphasizing its potential in remittances, cross-border payments, and emerging economies.
Practical Applications of Bitcoin
Bitcoin’s application extends far beyond consumer-facing transactions. Its potential lies in diverse sectors, including finance, supply chain management, and even voting systems. The core principles of decentralization and transparency underpin its unique value proposition in various contexts.
Bitcoin, a popular cryptocurrency, often requires interaction with a cryptocurrency exchange to buy or sell. These exchanges, like cryptocurrency exchange platforms, facilitate the trading of various cryptocurrencies, including bitcoin. Ultimately, bitcoin’s value and accessibility remain tied to the availability and efficiency of these exchange services.
- Micropayments: Bitcoin’s ability to handle small-value transactions facilitates micropayments, opening opportunities in areas like online content subscriptions, in-app purchases, and digital goods.
- Cross-border Payments: Bitcoin offers an efficient alternative to traditional remittance services, reducing transaction fees and processing times for international money transfers.
- Supply Chain Management: Tracking goods through the supply chain using blockchain technology, including Bitcoin, can enhance transparency and accountability.
- Investment and Portfolio Diversification: Bitcoin is increasingly recognized as a viable asset class for diversifying investment portfolios, offering unique returns compared to traditional financial instruments.
- Gaming and NFTs: The potential of Bitcoin extends to the gaming industry, enabling in-game purchases and the creation of non-fungible tokens (NFTs), adding value and utility to virtual assets.
- Digital Identity Verification: Bitcoin’s potential extends to the digital realm, where it can serve as a decentralized and secure means of verifying digital identities, improving security and reducing fraud.
Bitcoin for Remittances and Cross-Border Payments
Bitcoin’s inherent capabilities offer substantial advantages over traditional remittance systems, particularly in regions with limited banking infrastructure. Lower transaction fees and faster processing times are significant factors in its appeal.
- Reduced Transaction Fees: Bitcoin transactions often incur significantly lower fees compared to traditional wire transfers, potentially saving substantial amounts for individuals sending money internationally.
- Faster Processing Times: Bitcoin transactions, processed on the blockchain, typically complete within minutes, drastically improving speed compared to the days or weeks it can take for traditional methods.
- Increased Accessibility: Bitcoin’s decentralized nature can bypass traditional financial intermediaries, enabling transactions even in areas with limited banking access.
Examples of Businesses Utilizing Bitcoin
Several businesses have embraced Bitcoin for their operations, leveraging its efficiency and transparency. This adoption reflects the increasing recognition of Bitcoin’s value beyond speculative investments.
- Overstock.com: The online retailer accepts Bitcoin as a payment method, offering customers an alternative to traditional payment options.
- MicroStrategy: This publicly traded business has significantly invested in Bitcoin as part of its treasury strategy, recognizing its potential as a store of value.
- Tesla: Tesla, a global automotive manufacturer, briefly accepted Bitcoin as a payment method, highlighting the growing recognition of its role in the wider economy.
Potential Use Cases in Emerging Economies
The potential of Bitcoin in emerging economies is substantial, addressing challenges faced by traditional financial systems. It has the potential to facilitate economic development in underserved regions.
- Financial Inclusion: Bitcoin can provide access to financial services for populations in underserved areas, particularly in regions with limited banking infrastructure.
- Economic Growth: The reduced transaction costs and faster payment times can stimulate trade and investment, fostering economic growth in emerging markets.
- Reducing Corruption: Bitcoin’s transparent nature, recorded on a public ledger, can potentially reduce the opportunities for corruption in government transactions and payments.
Closing Summary
In conclusion, Bitcoin cryptocurrency’s journey has been marked by innovation and controversy. Its potential to revolutionize finance is undeniable, but careful consideration of its environmental impact, regulatory landscape, and market volatility is crucial. This discussion has provided a comprehensive overview of the multifaceted nature of Bitcoin, leaving readers with a nuanced understanding of its place in the evolving financial world.
Commonly Asked Questions
What are the primary benefits of using Bitcoin?
Bitcoin offers potential benefits such as peer-to-peer transactions, reduced transaction fees compared to traditional systems, and global accessibility. However, factors like volatility and regulatory uncertainties should be considered.
How does Bitcoin’s blockchain technology work?
Bitcoin’s blockchain is a decentralized, public ledger that records all transactions. This ensures transparency and security through cryptographic hashing and consensus mechanisms.
What are the potential risks associated with Bitcoin investment?
Bitcoin’s price volatility is a significant risk. Speculative investment and market fluctuations can lead to substantial gains or losses. Thorough research and understanding of market trends are vital for responsible investment.






