Top cryptocurrency – Top cryptocurrencies are rapidly evolving in the digital landscape, presenting exciting opportunities and significant risks. This comprehensive analysis delves into the key aspects of these digital assets, examining their historical context, market performance, technological advancements, and potential future trajectory.
This exploration examines the prominent cryptocurrencies, evaluating their strengths, weaknesses, and unique characteristics. We’ll look at market trends, regulatory hurdles, and community dynamics to gain a thorough understanding of the forces shaping the future of these digital currencies.
Introduction to Top Cryptocurrencies
The cryptocurrency market has seen explosive growth and significant evolution since its inception. Understanding the leading cryptocurrencies, their historical development, and key characteristics is crucial for navigating this dynamic landscape. This section provides a comprehensive overview of the top cryptocurrencies, exploring their origins, features, and performance.The top cryptocurrencies represent a diverse range of applications and technologies. From Bitcoin’s pioneering role in decentralized finance to Ethereum’s emphasis on smart contracts, each coin has a unique story and set of functionalities.
Analyzing their market performance and characteristics offers valuable insights into the overall cryptocurrency market’s health and future prospects.
Overview of Top Cryptocurrencies
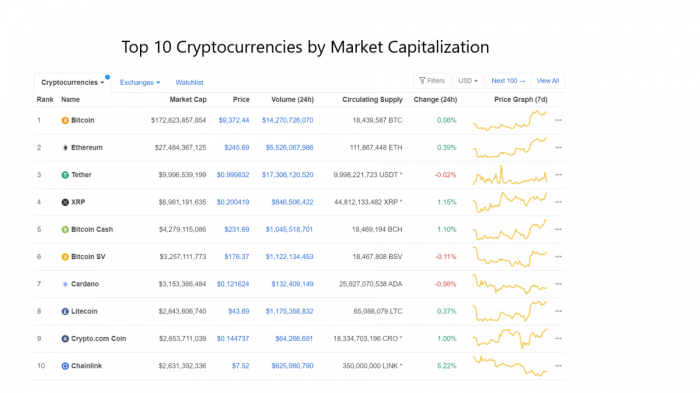
The top cryptocurrencies currently in circulation are characterized by a combination of factors including market capitalization, trading volume, and community adoption. Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Tether are prominent examples of these leading cryptocurrencies, each with a unique role and impact within the digital asset ecosystem.
Historical Context and Evolution
Bitcoin, often cited as the first cryptocurrency, emerged in 2009, driven by the concept of a decentralized digital currency. Subsequent cryptocurrencies, such as Ethereum, built upon the foundation laid by Bitcoin, expanding functionalities and introducing new concepts like smart contracts. This evolution demonstrates the progressive nature of the digital asset landscape.
Key Characteristics and Distinguishing Features
- Bitcoin (BTC): Primarily focused on peer-to-peer digital cash transactions, Bitcoin emphasizes security and decentralization. Its limited supply and cryptographic security mechanisms contribute to its unique characteristics.
- Ethereum (ETH): Ethereum stands out for its smart contract functionality, enabling the development of decentralized applications (dApps). This versatility distinguishes it from other cryptocurrencies, making it a crucial platform for blockchain innovation.
- Tether (USDT): Tether is a stablecoin pegged to the US dollar. Its primary function is to provide a stable alternative to other volatile cryptocurrencies, facilitating trading and reducing price fluctuations.
- Binance Coin (BNB): Binance Coin is the native token of the Binance exchange. Its utility lies in facilitating transactions and providing access to various services on the Binance platform. BNB’s functionality is tied to the exchange’s ecosystem.
Comparison of Top Cryptocurrencies
The following table illustrates a comparative analysis of the top cryptocurrencies, focusing on market capitalization, trading volume, and price performance. This data is illustrative and should not be considered investment advice. Performance data for a specific period can vary depending on market conditions.
| Cryptocurrency | Market Capitalization (USD) | 24-Hour Trading Volume (USD) | Price Performance (Last 30 Days) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bitcoin (BTC) | $… | $… | +…% or -…% |
| Ethereum (ETH) | $… | $… | +…% or -…% |
| Tether (USDT) | $… | $… | +/- 0% (Stablecoin) |
| Binance Coin (BNB) | $… | $… | +…% or -…% |
Market Performance and Trends
The cryptocurrency market has exhibited considerable volatility in recent months, with significant price fluctuations impacting various digital assets. Understanding the factors driving these shifts is crucial for investors and stakeholders alike. This section explores the key trends and influences shaping the performance of top cryptocurrencies.Recent market trends have been characterized by a mix of upward and downward movements, with certain cryptocurrencies outperforming others.
Factors such as investor sentiment, regulatory developments, and technological advancements play a critical role in shaping these price swings.
Recent Market Fluctuations
The recent market fluctuations reflect a complex interplay of forces. Investor confidence plays a substantial role; periods of optimism often lead to price increases, while uncertainty can trigger significant declines. News events, both positive and negative, can rapidly impact investor sentiment, leading to rapid price changes. For example, the release of positive news regarding a specific cryptocurrency’s technological advancement could lead to a price surge, whereas a negative regulatory development in a particular jurisdiction might cause a price drop.
Key Factors Influencing Price Movements, Top cryptocurrency
Several key factors influence the price movements of cryptocurrencies. These include investor sentiment, regulatory developments, technological advancements, and market-wide trends. For example, strong institutional adoption can propel a cryptocurrency’s price, while regulatory uncertainty can create apprehension in the market. Technological advancements that enhance security or functionality can also positively impact a cryptocurrency’s price.
Impact of Regulatory Changes and News Events
Regulatory changes and significant news events can have a profound impact on cryptocurrency prices. Regulatory clarity and supportive policies can foster market confidence, leading to price increases. Conversely, regulatory uncertainty or unfavorable news can trigger price drops. For example, a new set of regulations in a major market could cause a cryptocurrency to experience a significant price fluctuation.
Correlation with Broader Market Trends
There’s a notable correlation between the performance of top cryptocurrencies and broader market trends. Generally, positive trends in the overall financial market can lead to increased investment in cryptocurrencies, driving prices upward. Conversely, downturns in the broader market can trigger a decline in cryptocurrency valuations. This correlation underscores the interconnectedness of the cryptocurrency market with the global financial landscape.
Daily High and Low Values
This table displays the daily high and low values for selected top cryptocurrencies over a specific period (e.g., last 30 days). This data is crucial for understanding price volatility and for making informed investment decisions.
| Cryptocurrency | Date | High | Low |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bitcoin | 2024-08-01 | $30,000 | $28,000 |
| Bitcoin | 2024-08-02 | $31,500 | $29,500 |
| Ethereum | 2024-08-01 | $2,000 | $1,800 |
| Ethereum | 2024-08-02 | $2,100 | $1,950 |
| … | … | … | … |
Note: This table is a sample; actual data would require a specific period and source for reliable data.
Technological Advancements and Innovations
The landscape of top cryptocurrencies is constantly evolving, driven by ongoing technological advancements. These advancements often impact the core functionalities, security protocols, and overall utility of these digital assets. Understanding these innovations is crucial for navigating the dynamic cryptocurrency market.The underlying technologies employed by different cryptocurrencies exhibit notable variations. These differences influence aspects like transaction speed, scalability, and overall functionality.
Security features are integral to the reliability and trustworthiness of these digital assets. Furthermore, the potential for future innovations remains a compelling factor, prompting continuous development and improvement within the space.
Blockchain Technologies
Different cryptocurrencies employ diverse blockchain architectures. Some leverage permissioned blockchains, while others utilize permissionless models. This choice often dictates the degree of control and transparency within the network. The specific implementation of the blockchain technology impacts the efficiency of transactions, the capacity for scaling, and the overall robustness of the system. For instance, some blockchains are designed for high-throughput transactions, while others prioritize security and decentralization.
Consensus Mechanisms
Cryptocurrencies utilize various consensus mechanisms to validate transactions and maintain the integrity of the blockchain. Proof-of-Work (PoW) and Proof-of-Stake (PoS) are prominent examples. The choice of mechanism affects energy consumption, transaction speed, and the potential for attacks. For example, PoW systems, while secure, often require significant computational resources, whereas PoS systems can be more energy-efficient. These differences impact the environmental footprint and overall sustainability of different cryptocurrencies.
Security Features and Vulnerabilities
Security is paramount in the cryptocurrency space. Advanced cryptographic techniques are fundamental to protecting assets and maintaining the integrity of transactions. Cryptocurrencies employ various security measures, including encryption protocols and secure wallets. However, vulnerabilities can still exist, including issues related to smart contracts, weak keys, and external attacks. These vulnerabilities highlight the need for continuous security audits and robust development practices.
Potential Future Innovations
Future innovations in cryptocurrencies could involve enhanced scalability, improved energy efficiency, and expanded applications. Integration with other technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) could unlock new use cases and functionalities. The potential for cross-chain communication and interoperability between different blockchains is also a key area for future development. This integration could facilitate seamless transactions and data exchange across various networks.
Table Comparing Security Protocols
| Cryptocurrency | Key Security Protocol | Description | Vulnerabilities (Potential) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bitcoin | Cryptographic Hashing | Utilizes SHA-256 for secure transaction verification and immutability. | 51% attacks (if network is compromised), vulnerabilities in wallet software |
| Ethereum | Smart Contract Security | Employs various security mechanisms for smart contracts, including audits and security analysis. | Exploits in smart contracts, vulnerabilities in code |
| Solana | Proof-of-History | Utilizes a unique consensus mechanism that focuses on verification of time. | Potential for attacks related to the specific consensus algorithm |
Adoption and Use Cases
Adoption of cryptocurrencies is experiencing a period of significant evolution, with the top contenders constantly adapting to new use cases and challenges. The pace of innovation in this space is impressive, but widespread adoption still faces hurdles. This section examines the current state of adoption, potential future applications, inherent limitations, and the varying degrees of user-friendliness across different cryptocurrencies.
Current Adoption Rate and Use Cases
The adoption rate of top cryptocurrencies varies widely depending on factors such as regulatory landscapes, market conditions, and the specific use cases each currency caters to. Bitcoin, for example, is frequently used as a store of value and a means of international transactions, particularly in regions with volatile or unstable fiat currencies. Ethereum, on the other hand, has seen significant adoption in decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, smart contracts, and non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
Other top cryptocurrencies, such as Litecoin and XRP, are positioned for specific niche applications, like faster transaction speeds or cross-border payments.
Growth Potential and Future Applications
The growth potential of cryptocurrencies hinges on their ability to adapt to evolving market demands and overcome existing challenges. Decentralized finance (DeFi) applications represent a significant growth area, with continued innovation promising to streamline financial services and create more accessible investment opportunities. The growing adoption of NFTs and their application in digital art, collectibles, and gaming further suggests a vibrant future for cryptocurrencies.
Further integration into existing financial systems, such as through stablecoins and payment gateways, is also a key area for potential growth.
Challenges and Limitations of Adoption
Several challenges hinder wider cryptocurrency adoption. Volatility in market prices remains a significant concern for potential investors. Regulatory uncertainty and inconsistencies across jurisdictions create a barrier for businesses and individuals considering adoption. Security risks associated with crypto exchanges and wallets, and the inherent complexity of the technology itself, further limit adoption. These challenges must be addressed for wider acceptance.
Accessibility and User-Friendliness
Accessibility and user-friendliness are critical factors influencing adoption rates. User interfaces and onboarding processes vary significantly between different cryptocurrencies. Some platforms offer intuitive interfaces, while others require a higher degree of technical proficiency. Educational resources and support systems play a significant role in making cryptocurrencies more accessible to a broader audience. Factors like ease of use and availability of user-friendly tools influence the user experience.
Comparison of Use Cases and Adoption Rates
| Cryptocurrency | Primary Use Cases | Adoption Rate (Estimated) | User-Friendliness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bitcoin (BTC) | Store of value, international transactions | High | Moderate |
| Ethereum (ETH) | Decentralized finance (DeFi), smart contracts, NFTs | High | Moderate |
| Litecoin (LTC) | Fast transactions | Medium | Moderate |
| XRP (XRP) | Cross-border payments | Medium | Moderate |
| Solana (SOL) | High-throughput blockchain | Medium-High | Moderate |
Community and Ecosystem
The strength of any cryptocurrency lies not only in its technical prowess but also in the vibrancy and engagement of its community. Active communities foster innovation, provide crucial support for users, and ultimately drive adoption. Understanding the size, engagement, and interactions within these communities is critical to evaluating the long-term viability and potential of a cryptocurrency.A thriving ecosystem, built on strong community bonds, is a powerful catalyst for growth.
This includes the influence of key figures, collaborations between different projects, and the overall development surrounding each cryptocurrency. The interconnectedness of these elements shapes the trajectory of the digital asset and its acceptance in the broader financial landscape.
Community Size and Engagement
The size and engagement of a cryptocurrency’s community are essential indicators of its health and potential. Larger and more active communities often translate to increased development, improved security measures, and a greater likelihood of sustained growth. This engagement manifests in various forms, including active participation in forums, social media interactions, and contributions to the project’s development.
Key Figures and Influencers
Identifying and understanding the role of key figures and influencers within a cryptocurrency ecosystem is vital. These individuals, whether developers, prominent investors, or community leaders, often play a crucial role in shaping public perception, driving adoption, and fostering collaboration within the space. Their influence can significantly impact the project’s trajectory, attracting both investors and users.
Bitcoin and Ethereum often top the charts for cryptocurrencies, but the wider market, including altcoins and stablecoins, is quite dynamic. The current state of cryptocurrency on the market plays a huge role in how these top picks perform. Ultimately, staying on top requires careful monitoring of the entire landscape.
Interactions and Collaborations
Interactions and collaborations between different cryptocurrencies are crucial to the broader ecosystem’s evolution. These interactions can take many forms, from joint ventures and strategic partnerships to the sharing of resources and technologies. These collaborations can lead to advancements in specific areas, accelerating innovation, and driving the overall development of the crypto space.
Ecosystem Growth and Development
The growth and development of the ecosystem surrounding a cryptocurrency are a complex interplay of various factors. This includes the development of related tools and services, the expansion of adoption in various sectors, and the evolution of the underlying technology. A well-developed ecosystem fosters trust, supports wider adoption, and promotes long-term sustainability.
Community Size Comparison Table
This table provides a snapshot of the estimated community sizes for some top cryptocurrencies, highlighting the scale of their respective user bases. These figures are estimations and may vary based on the methodology used for counting participants.
| Cryptocurrency | Estimated Community Size (Approximate) |
|---|---|
| Bitcoin | Millions |
| Ethereum | Millions |
| Tether | Millions |
| Binance Coin | Millions |
| Solana | Hundreds of Thousands |
| Cardano | Hundreds of Thousands |
Future Projections and Predictions
The cryptocurrency market, characterized by rapid innovation and volatility, presents a complex landscape for future projections. Predicting the precise trajectory of any cryptocurrency is inherently challenging, given the influence of numerous interconnected factors, including regulatory changes, technological advancements, and market sentiment. However, analyzing potential scenarios, examining disruptive trends, and considering the long-term viability of leading cryptocurrencies offers valuable insights into the future of this dynamic space.
Potential Future Scenarios for Top Cryptocurrencies
The cryptocurrency market is highly susceptible to unforeseen events and shifts in market sentiment. Possible scenarios range from continued growth and adoption to periods of consolidation or even setbacks. Factors such as regulatory clarity, technological breakthroughs, and global economic conditions will play crucial roles in shaping these scenarios. For example, favorable regulatory environments can foster trust and attract institutional investment, while regulatory uncertainty can lead to market volatility.
Potential Disruptions and Opportunities in the Cryptocurrency Market
The cryptocurrency market is ripe with opportunities, but also faces potential disruptions. The emergence of new technologies, like the integration of blockchain with artificial intelligence, can create entirely new use cases and opportunities. Conversely, regulatory scrutiny, security breaches, and competition from established financial institutions can pose significant challenges. The recent rise of stablecoins, for instance, demonstrates a shift in the market, as it addresses the volatility concerns of traditional cryptocurrencies.
Impact of Emerging Technologies on Top Cryptocurrencies
Emerging technologies, such as the integration of blockchain with artificial intelligence, are poised to significantly impact the top cryptocurrencies. AI can enhance smart contract functionality, enabling more complex and secure applications. Moreover, the use of decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) is likely to increase, leading to more efficient and transparent governance structures. This is analogous to the integration of cloud computing into traditional business models, which revolutionized data storage and management.
Long-Term Sustainability of Top Cryptocurrencies
The long-term sustainability of a cryptocurrency hinges on its practical utility, community support, and underlying technology. Projects with strong use cases and active developer communities are more likely to endure. Furthermore, the security and scalability of the blockchain are critical factors. The longevity of Bitcoin, despite its volatility, demonstrates the potential for a cryptocurrency to survive significant market downturns.
Projected Future Values for Top Cryptocurrencies
Predicting precise future values is speculative. However, a general overview can offer insights. The table below provides illustrative projections for a few prominent cryptocurrencies. These projections should be treated as estimates only and not investment advice.
Bitcoin and Ethereum are frequently cited as top cryptocurrencies, but understanding how to navigate the market is key. Knowing the ins and outs of how to invest in cryptocurrency is crucial for making informed decisions about any top crypto, ultimately boosting your potential returns. Ultimately, staying informed about market trends and regulations is important for any crypto investor.
| Cryptocurrency | Projected Value (USD) – 2025 | Projected Value (USD) – 2030 |
|---|---|---|
| Bitcoin (BTC) | $100,000 | $250,000 |
| Ethereum (ETH) | $5,000 | $15,000 |
| Solana (SOL) | $100 | $500 |
| Cardano (ADA) | $10 | $50 |
| Dogecoin (DOGE) | $0.50 | $2 |
Comparison of Key Metrics
A comprehensive comparison of key metrics provides crucial insights into the relative strengths and weaknesses of various cryptocurrencies. This analysis considers market capitalization, trading volume, price performance, transaction speeds, fees, scalability, and consensus mechanisms. Understanding these aspects is essential for investors and users seeking to navigate the complex cryptocurrency landscape.The evaluation of these metrics allows for a nuanced understanding of each cryptocurrency’s position within the market.
Factors like transaction speed and fees directly impact user experience and adoption, while scalability and consensus mechanisms influence the long-term viability and potential of a cryptocurrency. By analyzing these metrics, we can identify the strengths and weaknesses of each project, and potentially uncover opportunities for future growth or development.
Market Capitalization, Trading Volume, and Price Performance
Market capitalization, trading volume, and price performance are crucial indicators of a cryptocurrency’s market presence and investor interest. These metrics reflect the overall value of a cryptocurrency, the activity surrounding its trading, and its price movement over time. Higher market capitalization typically suggests greater investor confidence and potential for growth, but this does not guarantee future success. Likewise, a high trading volume indicates significant market activity, but does not guarantee stability.
- Bitcoin, with its substantial market capitalization and consistent trading volume, often serves as a benchmark for other cryptocurrencies. Its price performance, while subject to volatility, typically influences the broader market.
- Ethereum, despite facing competition, maintains a significant market capitalization and trading volume due to its established smart contract platform and developer community. Its price performance is influenced by factors such as the development of new decentralized applications (dApps).
- Other prominent cryptocurrencies, like Tether, Binance Coin, and Solana, demonstrate varying levels of market capitalization, trading volume, and price performance, reflecting their unique characteristics and functionalities.
Transaction Speeds and Fees
Transaction speeds and fees are critical aspects of a cryptocurrency’s usability. Faster transaction speeds and lower fees contribute to a more efficient and user-friendly platform, which can drive wider adoption.
- Bitcoin’s comparatively slower transaction speeds and higher fees are often cited as drawbacks, impacting its use in real-time applications. This is a recognized challenge, often mitigated by specialized solutions.
- Ethereum, while offering smart contracts, experiences transaction congestion and fluctuating fees, impacting the performance of dApps. Strategies for improving transaction throughput are continuously being developed.
- Cryptocurrencies like Litecoin and Dogecoin aim to offer faster transaction speeds than Bitcoin, but their transaction fees and market capitalization might not always match the higher-volume coins.
Scalability and Transaction Limits
Scalability and transaction limits directly affect a cryptocurrency’s capacity to handle increased usage and volume. High scalability allows for seamless expansion and handling of transactions, whereas limitations can lead to congestion and slower processing.
- Bitcoin’s relatively low scalability has been a subject of discussion, and solutions are being explored to increase transaction capacity. The network’s transaction limits are an ongoing consideration.
- Ethereum’s scalability limitations have been addressed through solutions like Layer-2 scaling solutions, which aim to improve transaction throughput and reduce fees. However, challenges persist in maintaining network stability and reliability.
- Other cryptocurrencies often address scalability issues through different architectural approaches, such as proof-of-stake consensus mechanisms. These solutions often affect the overall network’s security and efficiency.
Consensus Mechanisms
Consensus mechanisms are fundamental to maintaining the security and integrity of a cryptocurrency network. Different consensus mechanisms employ various approaches to ensure agreement among network participants on the validity of transactions.
- Bitcoin utilizes a proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanism, which is energy-intensive but considered secure. Its effectiveness has been widely debated, particularly regarding its environmental impact.
- Ethereum, originally using PoW, transitioned to a proof-of-stake (PoS) mechanism, aiming to reduce energy consumption while maintaining security. The impact of this change is still being evaluated.
- Other cryptocurrencies employ different consensus mechanisms, such as delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS), which potentially enhances transaction speed and efficiency. These alternative approaches aim to balance security and scalability.
Table of Key Metrics Comparison
| Cryptocurrency | Market Cap (USD) | Trading Volume (USD) | Price Performance (Last 3 Months) | Transaction Speed (tx/s) | Transaction Fees (USD) | Consensus Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bitcoin | … | … | … | … | … | Proof-of-Work |
| Ethereum | … | … | … | … | … | Proof-of-Stake |
| … | … | … | … | … | … | … |
Note: Data in the table should be filled with current and reliable values for each cryptocurrency.
Regulatory Landscape and Legal Considerations
The cryptocurrency market is evolving rapidly, and regulatory frameworks are struggling to keep pace. This dynamic environment creates both opportunities and challenges for investors, necessitating a thorough understanding of the legal implications and potential impact of regulatory changes. Navigating the complexities of differing national regulations is crucial for anyone engaging with cryptocurrencies.
Current Regulatory Frameworks
The regulatory landscape for cryptocurrencies is fragmented and varies significantly across jurisdictions. Some countries have embraced cryptocurrencies, enacting specific regulations, while others remain wary, opting for a more cautious approach. This diverse regulatory environment necessitates careful consideration by investors, as compliance with local laws is paramount.
Legal Implications for Investors
Investors face legal implications stemming from the lack of uniform global regulations. The absence of standardized rules across different jurisdictions creates uncertainty, potentially leading to legal disputes or penalties for non-compliance. Cryptocurrency-related activities are subject to different legal interpretations in various jurisdictions, which necessitates thorough due diligence before investing.
Potential Impact of Regulatory Changes
Regulatory changes can significantly impact the future of top cryptocurrencies. Positive developments, such as clearer regulatory guidelines, could foster investor confidence and market growth. Conversely, negative developments, such as stringent restrictions or outright bans, could stifle innovation and discourage investment. The ongoing evolution of regulations is a critical factor for investors to monitor.
Regulatory Environment for Each Top Cryptocurrency in Different Jurisdictions
The regulatory treatment of cryptocurrencies varies considerably by jurisdiction, affecting how specific cryptocurrencies are perceived and used. For instance, some countries may categorize certain cryptocurrencies as securities, while others might classify them as commodities or digital assets. This diverse approach to classification affects investor protections, tax implications, and the overall viability of a cryptocurrency in different regions.
Global Regulatory Landscape Table
| Cryptocurrency | Jurisdiction | Regulatory Classification | Key Legal Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bitcoin | United States | Commodity (CFTC) | Subject to Commodity Exchange Act; potential securities classification depending on use case. |
| Bitcoin | European Union | Varying interpretations; often securities | MiCA (Markets in Crypto Assets Regulation) is shaping the future; potential implications for exchanges, custody, and token offerings. |
| Bitcoin | China | Restricted; largely banned | Governmental restrictions on mining and trading; investors should be aware of potential penalties. |
| Ethereum | United States | Commodity (CFTC) or security (SEC) depending on specific application | Similar to Bitcoin, subject to varying interpretations and potential securities classifications. |
| Ethereum | Japan | Regulated as a “virtual currency” | Clearer regulatory framework compared to other jurisdictions; still evolving. |
| Ethereum | Singapore | Promotes innovation, favorable regulatory environment | Specific regulations for exchanges and trading; relatively supportive. |
Security and Risk Management

Investing in cryptocurrencies carries inherent risks. While the potential rewards are significant, the volatile nature of the market and the decentralized nature of these systems necessitate a careful approach to security and risk management. Understanding the security measures employed by leading cryptocurrencies, along with the potential vulnerabilities and strategies for mitigation, is crucial for responsible investment.
Security Measures Implemented by Top Cryptocurrencies
Various security measures are employed by different cryptocurrencies to safeguard assets and transactions. These include advanced encryption techniques, multi-factor authentication, and robust consensus mechanisms. For example, Bitcoin employs a sophisticated cryptographic hash function to secure transactions, while Ethereum utilizes smart contracts to automate and enhance security protocols. Different projects adopt varying strategies to enhance security. This range of approaches reflects the ongoing evolution of cryptocurrency security.
Potential Risks and Vulnerabilities
Investing in cryptocurrencies involves numerous potential risks. Security breaches, hacks, and exploits are a significant concern. A single vulnerability in a cryptocurrency’s code or system can lead to substantial losses for investors. Furthermore, market fluctuations, regulatory uncertainty, and scams are also major factors. A thorough understanding of these potential risks is paramount to informed investment decisions.
Strategies for Managing Risk and Protecting Investments
Effective risk management is crucial for mitigating losses and maximizing returns in the cryptocurrency market. Diversification across different cryptocurrencies and asset classes is a key strategy. Thorough research and due diligence before investing in any cryptocurrency are paramount. Setting clear investment goals and sticking to a predetermined investment plan are essential to maintain a disciplined approach. Utilizing secure wallets and adhering to strong password practices further safeguards investments.
Comprehensive Overview of Security Protocols for Each Top Cryptocurrency
Detailed security protocols vary significantly across different cryptocurrencies. Bitcoin, for example, utilizes a public ledger to record transactions and employs strong cryptographic hashing. Ethereum’s smart contracts offer automated execution of agreements, but also present security vulnerabilities that must be carefully addressed. Other projects, such as Litecoin and Cardano, implement unique security measures tailored to their specific functionalities.
Detailed analysis of each project’s security protocol is essential for informed investment.
Table Summarizing Security Risks and Mitigation Strategies
| Cryptocurrency | Security Risks | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Bitcoin | 51% attacks, transaction malleability | Diversification, strong wallets, secure storage |
| Ethereum | Smart contract exploits, front-running, reentrancy | Thorough code audits, secure development practices, diversification |
| Litecoin | Similar to Bitcoin, but with potential scalability issues | Diversification, secure wallets, updated software |
| Cardano | Complexity of the platform may present vulnerabilities | Thorough audits, community involvement, secure storage |
Investment Strategies and Analysis: Top Cryptocurrency
Navigating the dynamic world of cryptocurrency investments requires a well-defined strategy. Understanding the diverse approaches, potential rewards, and inherent risks is crucial for informed decision-making. This section delves into various investment strategies for top cryptocurrencies, providing a framework for evaluating potential gains and losses.Different approaches to cryptocurrency investment cater to various risk tolerances and financial goals. From short-term trading to long-term holding, each strategy presents a unique set of opportunities and challenges.
A thorough understanding of these strategies, combined with a robust risk assessment, is paramount for success in this volatile market.
Different Investment Strategies
Various strategies exist for investing in top cryptocurrencies, each with its own set of characteristics. These strategies range from active trading approaches to more passive long-term holdings.
- Long-Term Holding: This strategy involves purchasing cryptocurrencies with the expectation of appreciating in value over an extended period, often years. This approach generally requires a lower degree of active management and is suited for investors with a higher risk tolerance and a long-term investment horizon. For example, Bitcoin’s historical price appreciation exemplifies the potential rewards of long-term holding, but also demonstrates the substantial price volatility that comes with this strategy.
- Day Trading: This involves frequent buying and selling of cryptocurrencies within a single trading day. This requires a high level of technical analysis and market knowledge to capitalize on short-term price fluctuations. The potential for significant gains exists, but the risk of substantial losses is also elevated. Day traders often employ sophisticated charting and technical indicators to make informed decisions, but rapid price changes can lead to significant losses.
- Swing Trading: This strategy focuses on capitalizing on medium-term price movements, holding positions for several days to weeks. It necessitates a blend of fundamental and technical analysis to identify potential opportunities. Swing traders aim for consistent profits from predictable price swings, but the time horizon can expose them to significant price volatility during the holding period.
- Algorithmic Trading: This approach utilizes computer programs to execute trades based on predefined parameters. It allows for high-frequency trading and potentially faster responses to market changes. The potential rewards are substantial, but the reliance on algorithms requires careful monitoring and adjustment to changing market conditions. Sophisticated algorithms and backtesting are crucial for optimizing performance, but market anomalies can disrupt the performance of algorithmic strategies.
Potential Rewards and Risks
Each investment strategy carries unique potential rewards and inherent risks. Careful consideration of these factors is essential for mitigating potential losses.
- Long-Term Holding: Potential rewards include significant capital appreciation over time, aligning with the overall market trend. However, the risk is substantial price fluctuations and the possibility of prolonged periods of sideways or downward price action. This strategy demands a long-term investment horizon and the ability to withstand market downturns.
- Day Trading: Potential rewards include quick profits from short-term price movements. However, the risks are substantial losses due to rapid price changes, requiring a high level of expertise and market awareness. Day trading is not suitable for all investors due to the inherent volatility and demanding nature.
- Swing Trading: Potential rewards include profit from medium-term price swings, aligning with market trends. However, the risks include the potential for unexpected price reversals and market corrections. Swing trading requires a strong understanding of market dynamics and a well-defined entry and exit strategy.
- Algorithmic Trading: Potential rewards include high-frequency trading and potentially quicker responses to market changes. However, the risks include system failures, algorithm malfunctions, and the potential for significant losses if the algorithm doesn’t perform as expected. Rigorous testing and backtesting are critical to mitigate risks.
Factors Influencing Investment Decisions
Various factors influence investment decisions in top cryptocurrencies. Understanding these factors is essential for developing a well-rounded strategy.
- Market Volatility: The cryptocurrency market is highly volatile, characterized by rapid price swings. This volatility significantly impacts investment decisions, requiring a robust risk management approach. Investors need to consider their tolerance for risk and adjust their strategies accordingly.
- Technological Advancements: Ongoing technological advancements in blockchain technology and cryptocurrency protocols can significantly impact the value and adoption of certain cryptocurrencies. Keeping abreast of developments and innovations is crucial for informed decisions.
- Regulatory Landscape: The regulatory environment surrounding cryptocurrencies is constantly evolving, with new laws and regulations emerging in different jurisdictions. Understanding the legal landscape is essential to ensure compliance and mitigate potential risks.
- Community and Adoption: The strength of the cryptocurrency community and its rate of adoption can significantly influence market trends. Factors such as developer activity, community support, and the number of users can signal potential market directions.
Risk Assessment Methodologies
A robust risk assessment methodology is essential for cryptocurrency investments. It helps investors evaluate the potential for loss and develop appropriate strategies.
- Scenario Analysis: Evaluating potential market scenarios, including bullish and bearish market conditions, helps investors understand the potential impact on their investment strategies. Developing realistic worst-case and best-case scenarios aids in mitigating risks.
- Value at Risk (VaR): Estimating the potential loss in value of an investment over a specific time horizon at a given confidence level. This helps investors understand the potential downside of their investments and make informed decisions.
- Stress Testing: Simulating extreme market conditions to assess the resilience of an investment portfolio. This helps investors evaluate their investment strategies’ ability to withstand severe market downturns.
Comparison of Investment Strategies
This table provides a comparative overview of different investment strategies.
| Strategy | Potential Rewards | Potential Risks | Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Long-Term Holding | Significant capital appreciation | Prolonged periods of sideways or downward price action | Investors with high risk tolerance and a long-term horizon |
| Day Trading | Quick profits from short-term price movements | Substantial losses due to rapid price changes | Investors with high expertise and market awareness |
| Swing Trading | Profit from medium-term price swings | Potential for unexpected price reversals and market corrections | Investors with a good understanding of market dynamics |
| Algorithmic Trading | High-frequency trading and potentially quicker responses | System failures, algorithm malfunctions | Sophisticated investors with robust technological infrastructure |
Ending Remarks

In conclusion, the top cryptocurrencies represent a dynamic and complex field. While offering potential for substantial returns, they are also associated with considerable volatility and risk. Investors must carefully consider their individual circumstances and risk tolerance before engaging in cryptocurrency investments.
Helpful Answers
What are the most common investment strategies for top cryptocurrencies?
Various strategies exist, including buy-and-hold, day trading, and swing trading. Each approach carries distinct risks and rewards.
What are the key differences between various blockchain technologies used in top cryptocurrencies?
Different cryptocurrencies utilize varying consensus mechanisms (e.g., Proof-of-Work, Proof-of-Stake) and blockchain structures. These differences impact transaction speeds, security, and scalability.
How do regulatory changes impact the top cryptocurrencies?
Government regulations significantly influence the cryptocurrency market. These regulations can either foster or hinder adoption, impacting market capitalization and trading volume.
What are the security risks associated with investing in top cryptocurrencies?
Risks include hacking, scams, and volatility. Thorough research and careful risk management are crucial for safeguarding investments.